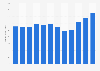
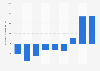
GM Cruise: operating income by quarter 2018-2024
General Motors reported an operating loss of *** million U.S. dollars from its subsidiary Cruise in the fourth quarter of 2024. The operation develops autonomous vehicle technology. Self-driving cars are yet to be commercially deployed; meanwhile, they consume large sums of research and development expenses. Fellow car manufacturer Honda had also invested in Cruise LLC. By late 2024, GM had decided to focus on its Super Cruise subscription prgram, moving away from its Cruise investments.
An empty driver's seat
The GM subsidiary received a permit from the Californian authorities in 2020 to remove human safety drivers from their autonomous vehicles (AV) in San Francisco. Driverless vehicles manufactured by the company could furthermore become a reality in other major U.S. cities at some point in 2021. As two of the largest AV patent owners in the United States as of November 2020, the GM–Honda joint venture will serve to develop innovations in platform-sharing and driver-assist technologies, at the same time enabling substantial cost savings.
An all-electric future
Currently, GM’s best-selling PEV in the United States is the Chevrolet Bolt, behind the popular Tesla models and Toyota’s Prius Prime. In 2020, GM announced that it is investing significantly in developing an all-electric-vehicle portfolio for the future, including a semi-autonomous sport utility vehicle (SUV). In general, standard SUV models have increased in popularity since the *****, with the United States, China, and Germany having emerged as the largest markets for SUV sales. It remains to be seen if all-electric SUV sales will be as successful in these three markets in coming years.