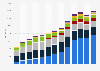
Energy-related CO2 emissions APAC 2014-2023
In 2023, the total carbon dioxide emissions in the Asia-Pacific region amounted to more than 21 billion metric tons. In addition to marking an increase from the previous year, this also represented an overall increase from about 17.62 billion tons of CO2 emitted in 2014.
APAC’s role in global CO2 emissions
China is by far the biggest CO2 emitter in the APAC region, releasing more carbon dioxide than all other countries in the region combined. Similarly, since the 1990s, Asia-Pacific has gone on to become the region with the biggest CO2 emissions globally, accounting for more than the combined total emissions of all other world regions, including the likes of North America and Europe. Looking at the volume of carbon dioxide emissions by sector, electricity and heat production is responsible for most of the emissions in Asia-Pacific as well as worldwide.
Impact on global warming
Emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as carbon dioxide are the main driver for climate change, as they critically increase the concentration of naturally occurring GHGs like CO2, which play an essential part in global climate by trapping the sun’s heat in the earth atmosphere. This is causing several concerning developments, including rising sea levels and increased risk of natural hazards such as typhoons, heavy rainfalls, and floods. With many territories particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, the Asia-Pacific region is looking for different ways to combat climate change, first and foremost investment in renewable energies.