Main energy transition targets for climate mitigation in France 2030-2050
In France, the high-priority targets to mitigate climate change were the reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, of final energy consumption, and the transition from fossil to renewable energy sources. The Energy Transition for Green Growth Act (enforced in August 2015) laid down different objectives for the years 2030 and 2050.
Targets breakdown
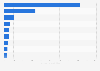
One of the long-term objectives was to reduce GHG emissions by ** percent between 1990 and 2030, and by ** percent between 1990 and 2050. To attain the 2030 reduction goal, total GHG emissions in France should drop by ** to *** million tons in only 10 years, between 2020 and 2030. In the past decades, emissions decreased by the same amount in 30 years, between 1990 and 2019.
The final energy consumption should be reduced by ** percent by 2050 with respect to 2012 levels, while primary energy usage from fossil fuels should decrease by ** percent and be replaced with renewable sources by 2030. The final energy consumption share by renewable sources in 2020 was still **** percentage points lower than the ** percent target.
Reduction of nuclear energy
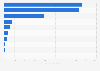
The nuclear share of electricity production was ** percent in 2021, making France one of the leading countries worldwide for nuclear power production. According to the Energy Transition Act, this share should be reduced to ** percent by 2025, while increasing renewables in the electricity budget. Nuclear plant safety is one of the main concerns in France, to such an extent that over ** percent of the respondents to a survey conducted in France in March 2021 declared themselves to be against nuclear power. In March 2023, the French National Assembly voted against the reduction of nuclear energy production in the country, abolishing this objective from the energy transition plan of France.