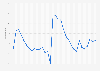
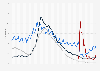
Mortgage delinquency rate in the U.S. 2000-2025, by quarter
Following the drastic increase directly after the COVID-19 pandemic, the delinquency rate started to gradually decline, falling below *** percent in the second quarter of 2023. In the second half of 2023, the delinquency rate picked up, but remained stable throughout 2024. In the first quarter of 2025, **** percent of mortgage loans were delinquent. That was significantly lower than the **** percent during the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 or the peak of *** percent during the subprime mortgage crisis of 2007-2010.
What does the mortgage delinquency rate tell us?
The mortgage delinquency rate is the share of the total number of mortgaged home loans in the U.S. where payment is overdue by 30 days or more. Many borrowers eventually manage to service their loan, though, as indicated by the markedly lower foreclosure rates. Total home mortgage debt in the U.S. stood at almost ** trillion U.S. dollars in 2024.
Not all mortgage loans are made equal
‘Subprime’ loans, being targeted at high-risk borrowers and generally coupled with higher interest rates to compensate for the risk. These loans have far higher delinquency rates than conventional loans. Defaulting on such loans was one of the triggers for the 2007-2010 financial crisis, with subprime delinquency rates reaching almost ** percent around this time. These higher delinquency rates translate into higher foreclosure rates, which peaked at just under ** percent of all subprime mortgages in 2011.