Worldwide capacity of marine energy 2009-2024
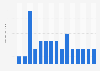
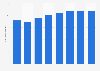
In 2024, the global capacity of marine energy reached 494 megawatts. This ocean energy is derived from the kinetic energy of ocean waves, tides, salinity, and differences in ocean temperatures.
Marine energy technologies
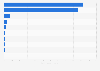
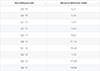
Marine energy is generated by the kinetic energy that can be harnessed from oceans as well as the salinity and temperature differences within the seas. Marine energy is often also referred to as ocean or hydrokinetic energy. It encompasses various forms of ocean energy, including tidal power which derives energy from moving masses of water and wave power which derives power from surface waves. Between 2010 and 2011, marine energy capacity doubled from 250 megawatts to 503 megawatts, respectively. Since then, global marine energy capacity has remained relatively stable. Currently, South Korea and France have the highest capacity of marine power in the world with holding about 255 and 212 megawatts of installed capacity, respectively.
In the United States, the Department of Energy has a Water Power Program to develop marine energy and technologies. As marine energy is still mostly in its infancy, this program focuses on technological development, market acceleration and deployment, and resource assessment and characterization. Theoretically, marine and hydrokinetics can deliver over 5,000 megawatts of potential energy in the United States. Among marine energy, energy derived from waves has the largest potential in the country, reaching up to 3,300 terawatt hours per year.